|
Abhishek Anand I am a postdoctoral research scientist in Westervelt Aerosol Group in Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory at Columbia University. I am building machine/deep learning models for estimating air pollutants using satellite-derived features and weather reanalysis parameters, validated with ground-level sensors in sub-Saharan Africa. I am further using the datasets to investigate health impacts to aid effective local policymaking. I graduated with Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from Carnegie Mellon University, where I worked with Prof. Albert Presto on developing low-cost techniques to measure atmospheric particulate matter and using air pollution data from low-cost monitors to identify emission sources. Additionally, I built a deep learning-based forecast model for fine particulate matter over Pittsburgh (USA) by using novel features from NASA's GEOS-CF and ground level measurements from a low-cost sensor network, spatially deployed over Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. I earned my M.Phil. and M.Sc. from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and B.Tech. in Civil Engineering from Indian Institute of Technology Delhi in New Delhi, India. Email / CV / Google Scholar / Linkedin / My Columbia Wesbite |

|
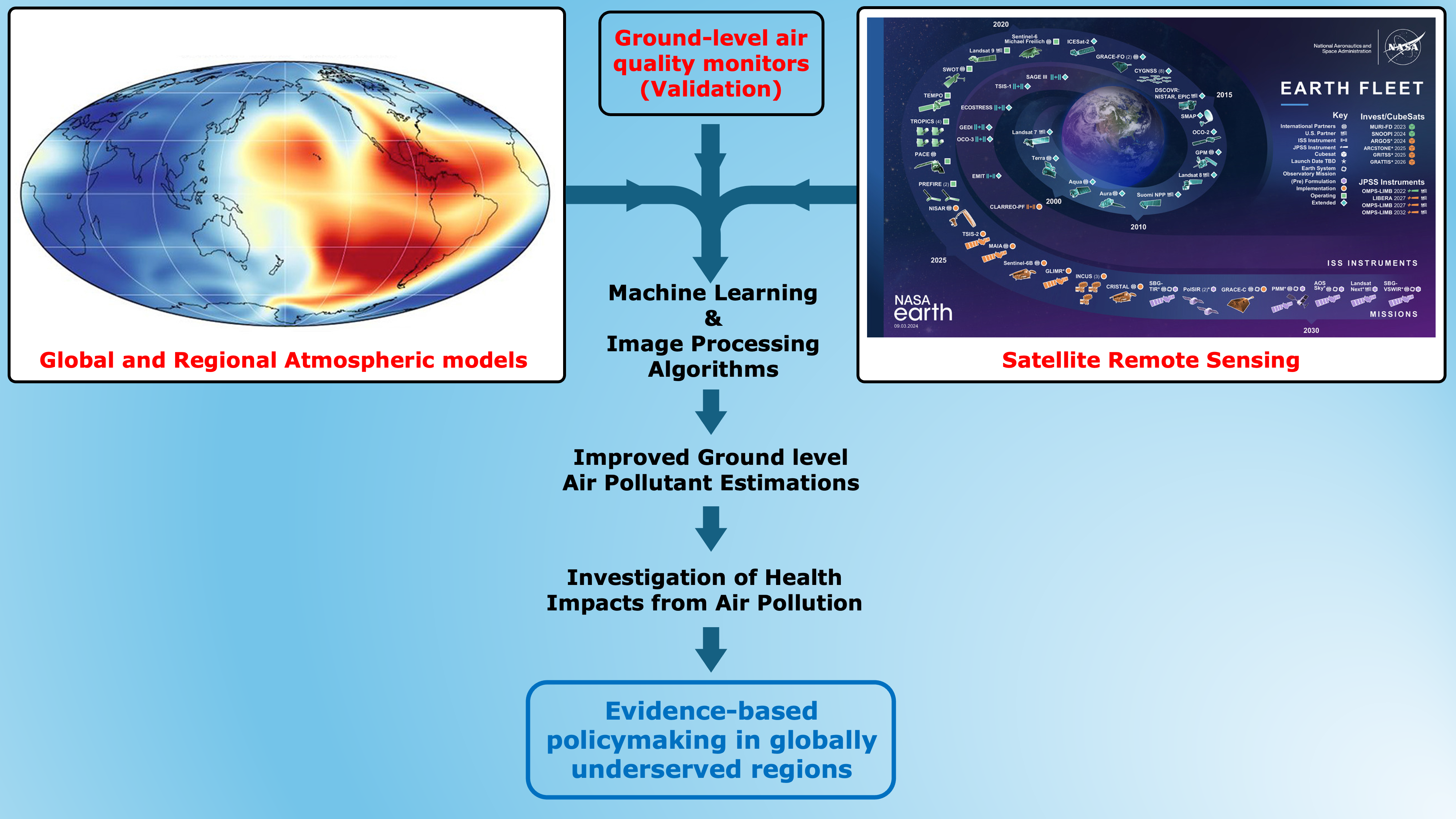
Research Interests
I'm interested in application of image processing and machine learning on remote sensing datasets, atmospheric simulations, and
investigating health impacts from air pollution.
Publications* represents corresponding author |
2025 |
|
|
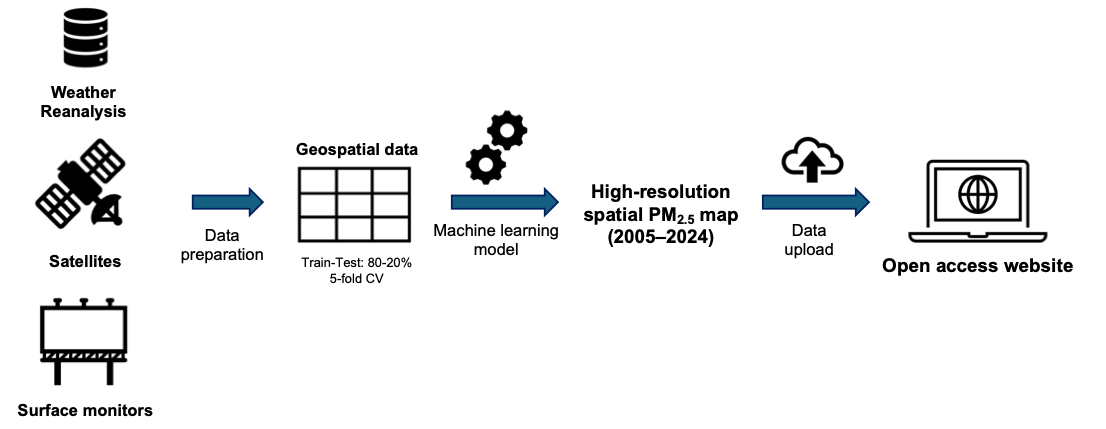
[Dataset] Gridded Daily PM2.5 at 1 km × 1 km Resolution from 2005–2024: Ghana
Abhishek Anand*, Joe Amooli, Daniel Westervelt Dataset published on Zenodo ( doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17920004 ) More project details available at Columbia University GRASP website This dataset provides daily estimates of surface PM2.5 concentrations across Ghana at a high spatial resolution of 1 km × 1 km. The data are generated by integrating satellite observations, ground-level monitors, and machine learning models, providing consistent spatiotemporal coverage over 20 years (2005-2024). |
|
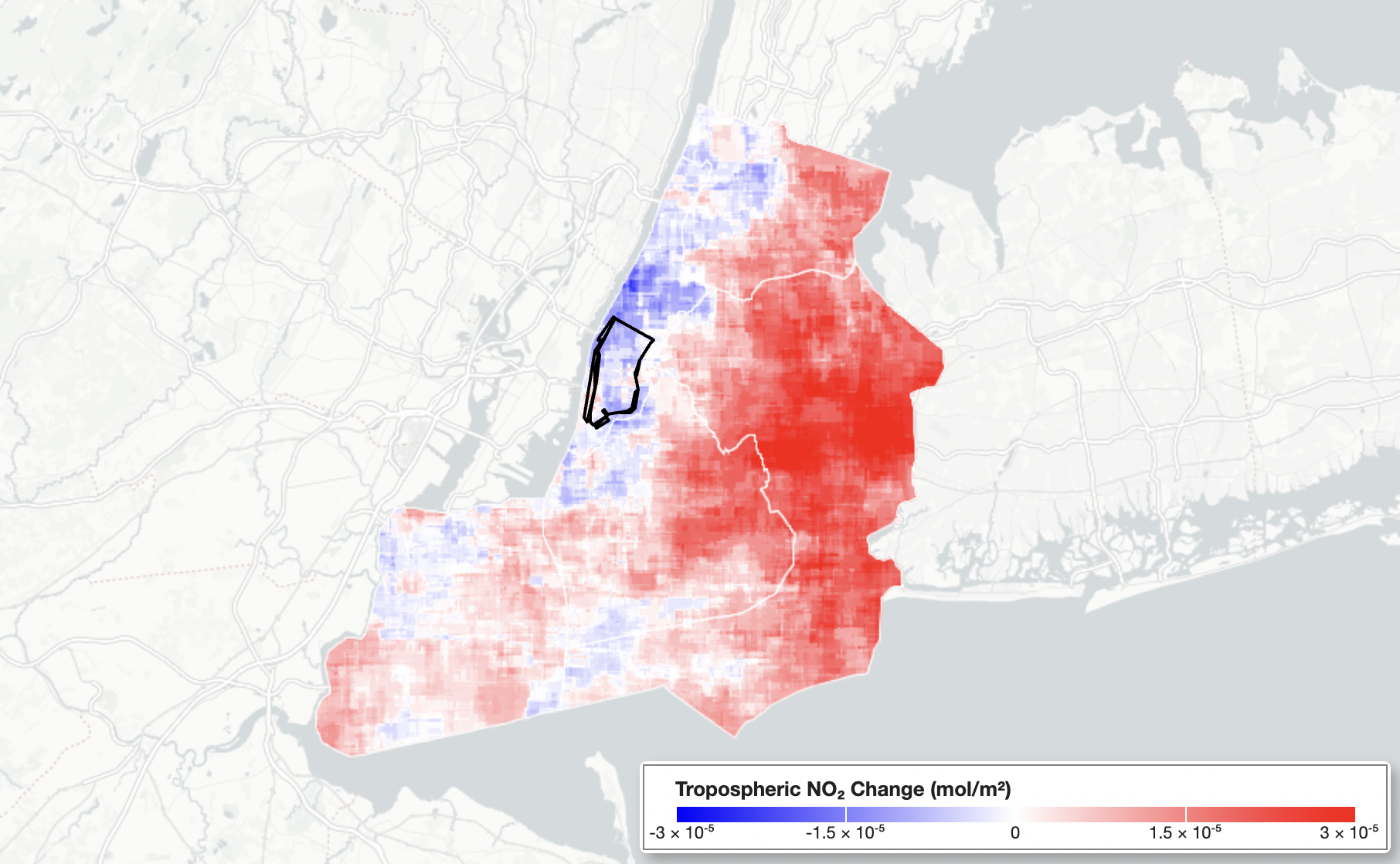
Variable Short-Term Air Quality Impacts of New York City’s Congestion Pricing Policy
Polina M. Goldberg, Abhishek Anand, Daniel Westervelt* Under review in Scientific Reports (*Preprint available) New York City implemented the Central Business District Tolling Program (CBDTP) on January 5, 2025 to reduce traffic and improve air quality in Manhattan. Using a difference-in-differences analysis, we assess short-term impacts of CBDTP on PM2.5 and NO2 across the five boroughs of New York City using ground-based NYCCAS monitors and satellite observations. |
|
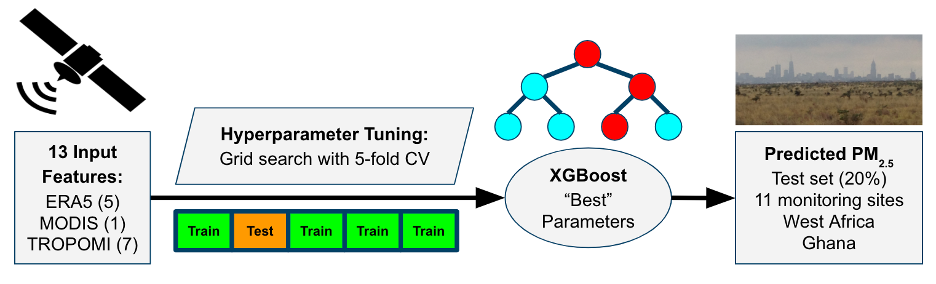
Twenty Years of High Spatiotemporal Resolution Estimates of Daily PM2.5 in West Africa Using Satellite
Data, Surface Monitors, and Machine Learning
Daniel Westervelt*, Joe Adabouk Amooli, Abhishek Anand ES&T Air, 2025 Air pollution is a major global health risk, especially in sub-Saharan Africa where monitoring is limited. We address this gap by developing machine/deep learning models using datasets for satellite-derived and weather reanalysis parameters to estimate daily PM2.5 for Ghana at 1 km resolution, spanning between 2005–2024. The model-derived PM2.5 were validated against measurements from an extensive network of surface monitors. |
2024 |
|
|
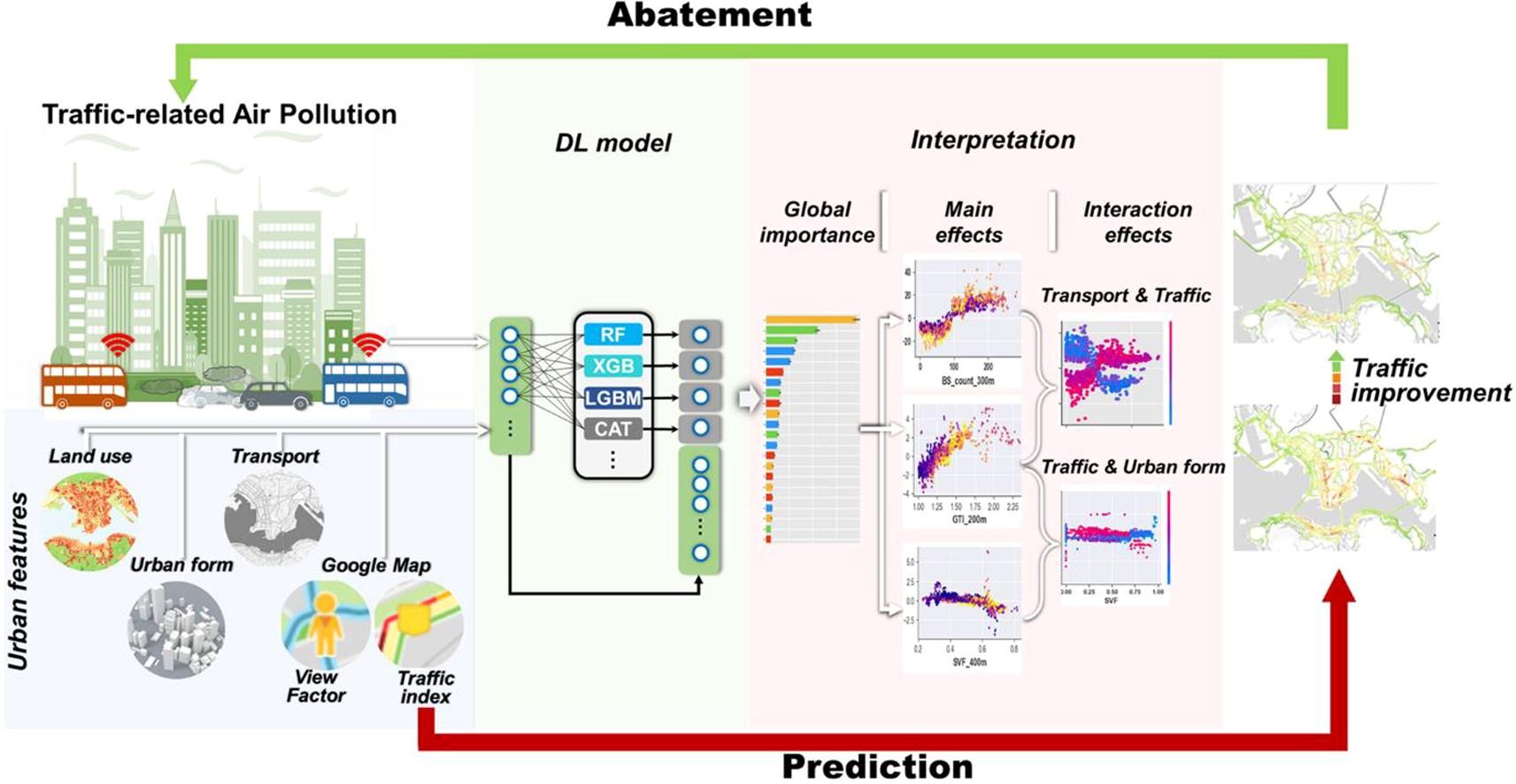
Combining Google traffic map with deep learning model to predict street-level traffic-related air pollutants in a complex urban environment
Peng Wei, Song Hao*, Yuan Shi*, Abhishek Anand, Ya Wang, Mengyuan Chu, Zhi Ning* Environment International, 2024 In this paper, we built deep learning model to predict fine scale NOx from traffic at street-level using data from mobile air quality sensors on buses and crowd-sourced Google real-time traffic status. |
|
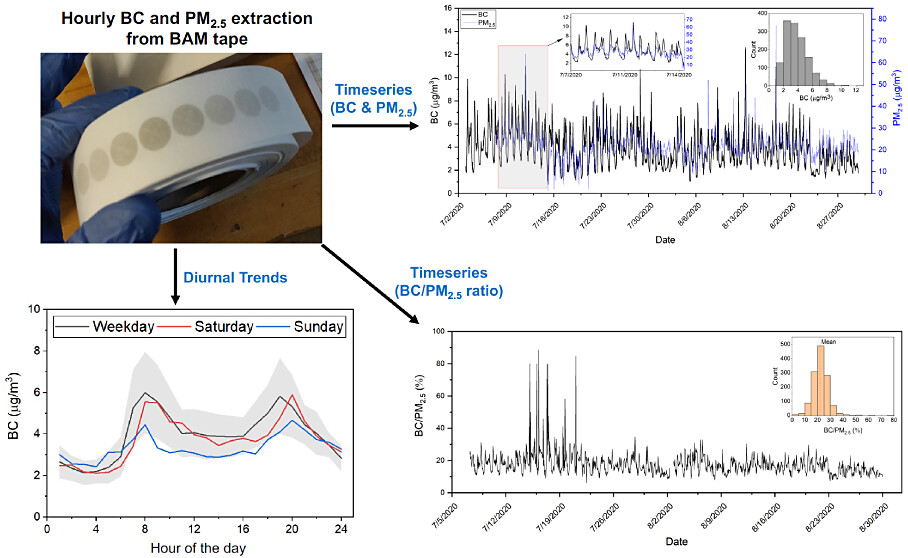
Low-Cost Hourly Ambient Black Carbon Measurements at Multiple Cities in Africa
Abhishek Anand, N’Datchoh Evelyne, Touré, Julien Bahino, ..., Albert A. Presto* Environmental Science & Technology, 2024 In this paper, we used the image processing method from Anand et al. (2023) on used filter tapes from Beta Attenuation Monnitors (BAMs) to measure atmospheric black carbon in African cities. |
2023 |
|
|
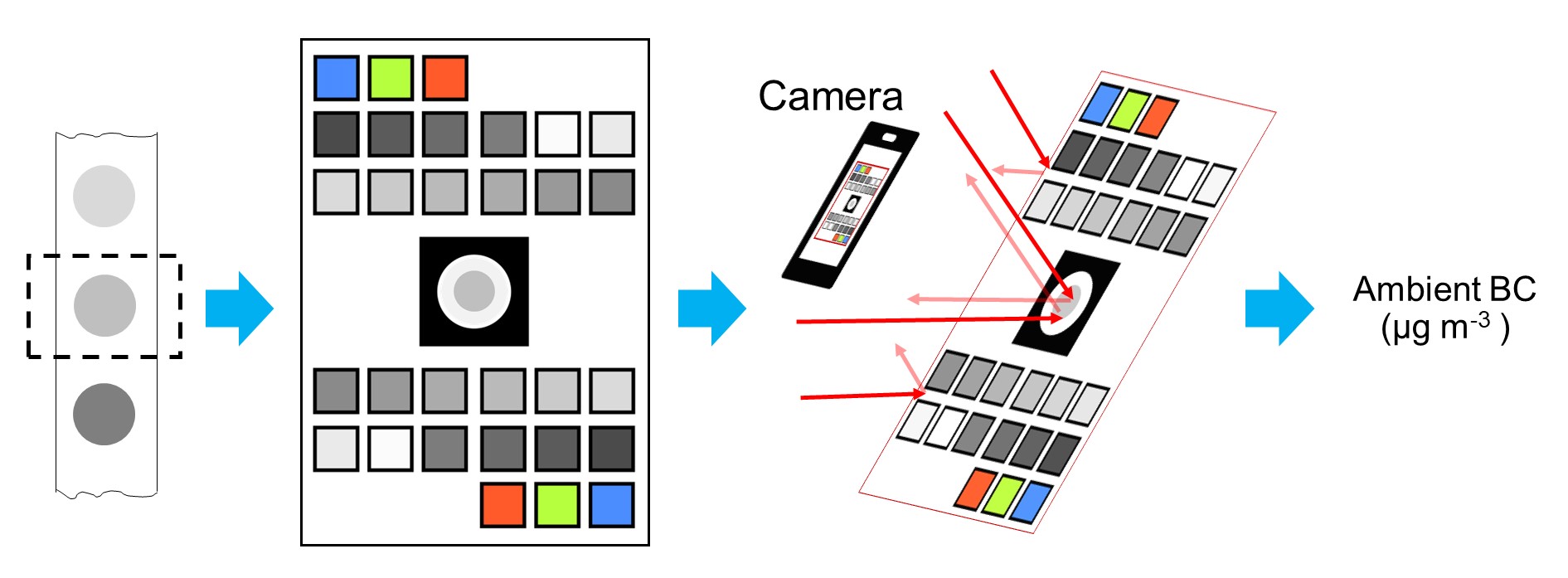
Estimation of hourly black carbon aerosol concentrations from glass fiber filter tapes using image reflectance-based method
Abhishek Anand, Suryaprakash Kompalli, Eniola Ajiboyec, Albert A. Presto* Environmental Science: Atmospheres, 2023
In this paper, we deployed computer vision to build an image processing method to estimate atmospheric black carbon from particulate
deposits on filter tapes.
|
2021 |
|
|
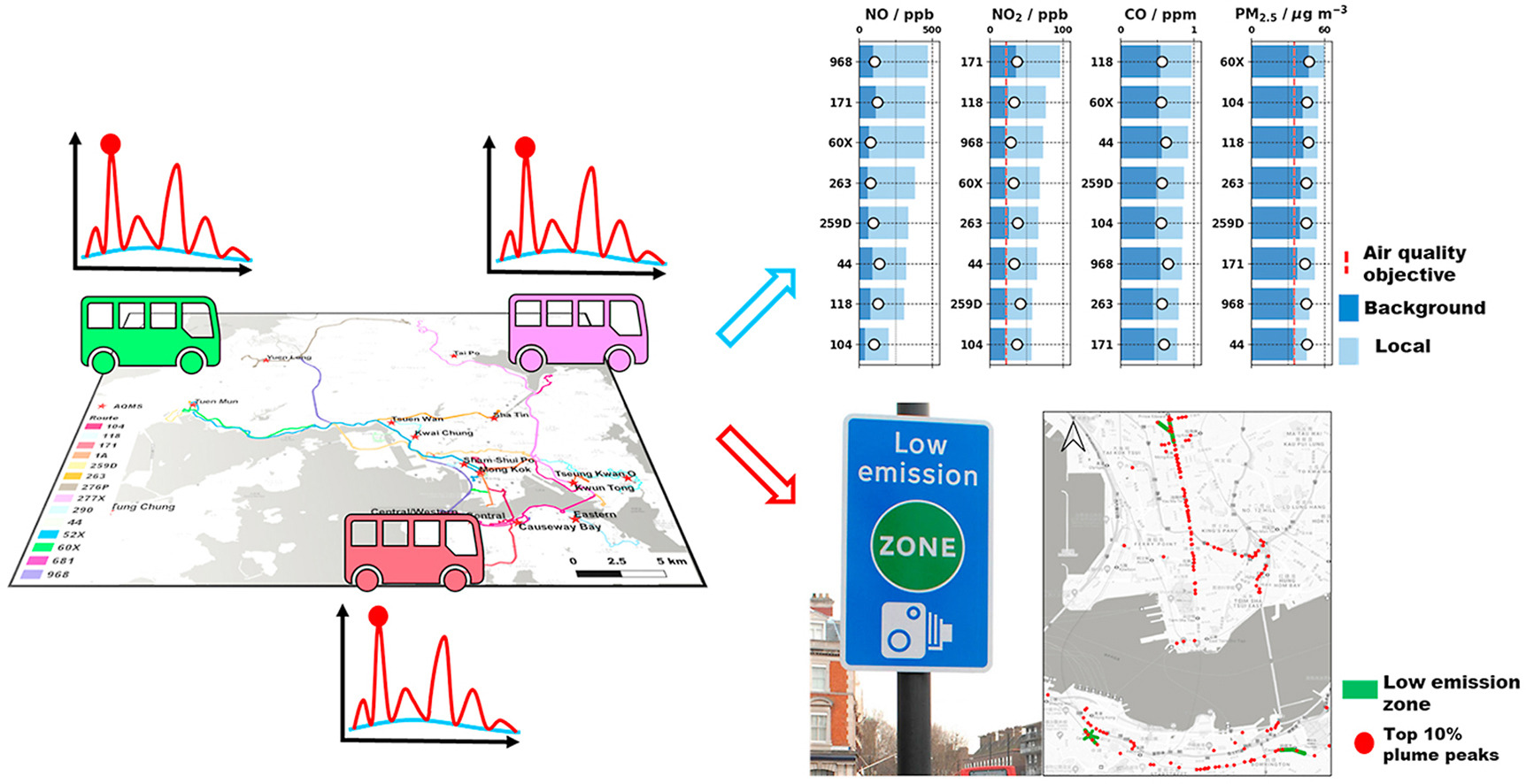
Determination of local traffic emission and non-local background source contribution to on-road
air pollution using fixed-route mobile air sensor network
Peng Wei, Peter Brimblecombe, Fenhuan Yang, Abhishek Anand, Yang Xing, Li Sun, Yuxi Sun, Mengyuan Chu, Zhi Ning* Environmental Pollution, 2021 In this paper, we deployed wavelet analysis and lowest percentile methods to quantify contributions of traffic-related emissions to on-road gaseous and particulate levels. |
2020 |
|
|
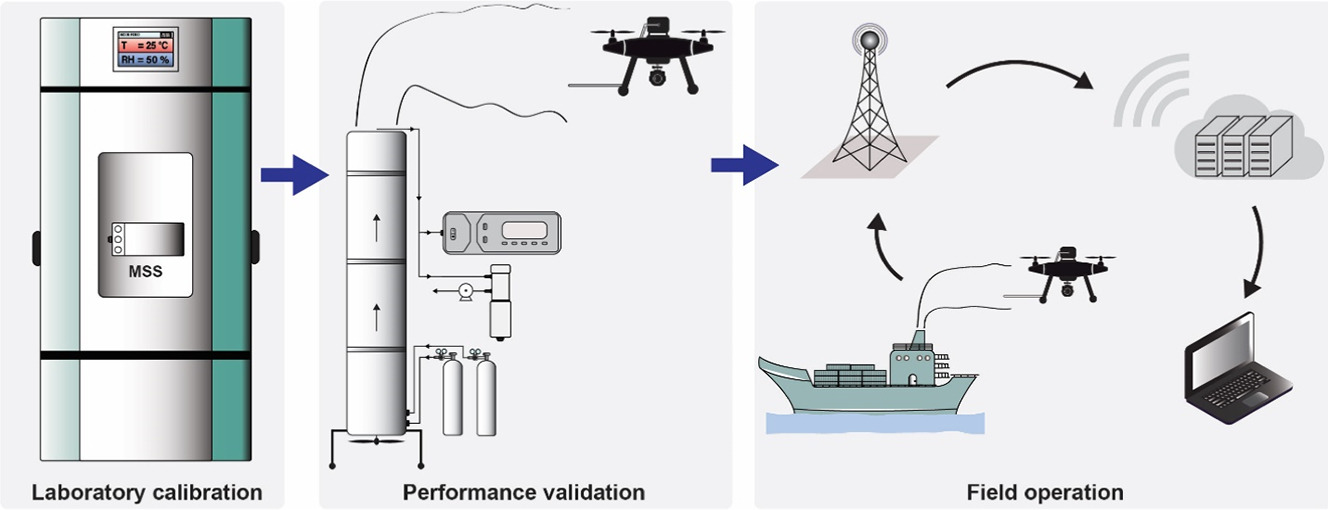
Protocol development for real-time ship fuel sulfur content determination using drone based plume sniffing microsensor system
Abhishek Anand, Peng Wei, Nirmal Kumar Gali, ..., Zhi Ning* Science of The Total Environment, 2020 In this paper, we developed an innovative solution for remotely measuring sulfur content in ship fuels from stack emissions with low-cost sensors attached on a drone. This work is aimed at effective policy implementation to reduce SO2 emissions from ships. |
|
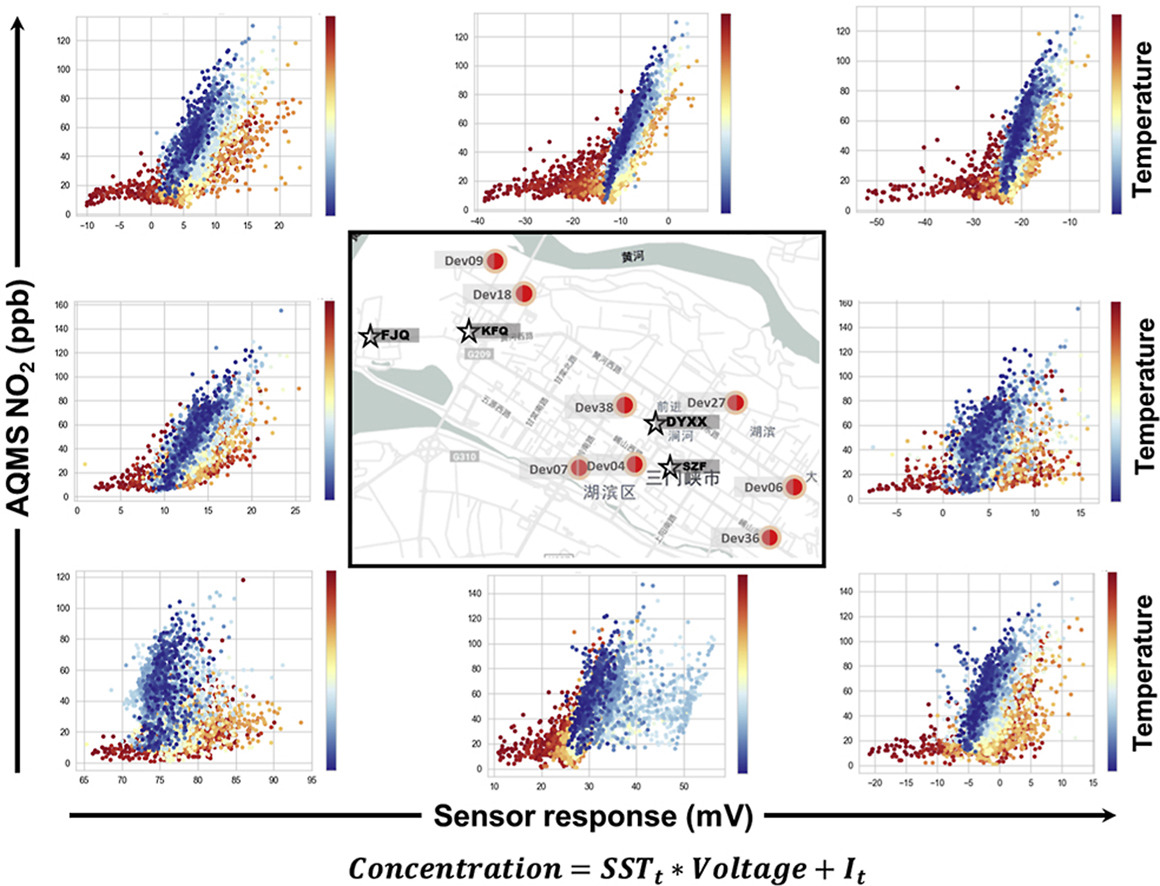
Development and evaluation of a robust temperature sensitive algorithm for long term NO2 gas sensor network data correction
Peng Wei, Li Sun, Abhishek Anand, Qing Zhang, Zong Huixin, Zhiqiang Deng, Ying Wang, Zhi Ning* Atmospheric Environment, 2020 In this paper, we propose a novel Temperature Look-Up (TLU) model for NO2 gas sensor outputs in case of long-term application, showing an improved performance over existing ML and MLR methods. |
News
December 2025
June 2025
May 2025
January 2025
August 2022
|